The first 600 alternating numbers :
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 81, 83, 85, 87, 89, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 101, 103, 105, 107, 109, 121, 123, 125, 127, 129, 141, 143, 145, 147, 149, 161, 163, 165, 167, 169, 181, 183, 185, 187, 189, 210, 212, 214, 216, 218, 230, 232, 234, 236, 238, 250, 252, 254, 256, 258, 270, 272, 274, 276, 278, 290, 292, 294, 296, 298, 301, 303, 305, 307, 309, 321, 323, 325, 327, 329, 341, 343, 345, 347, 349, 361, 363, 365, 367, 369, 381, 383, 385, 387, 389, 410, 412, 414, 416, 418, 430, 432, 434, 436, 438, 450, 452, 454, 456, 458, 470, 472, 474, 476, 478, 490, 492, 494, 496, 498, 501, 503, 505, 507, 509, 521, 523, 525, 527, 529, 541, 543, 545, 547, 549, 561, 563, 565, 567, 569, 581, 583, 585, 587, 589, 610, 612, 614, 616, 618, 630, 632, 634, 636, 638, 650, 652, 654, 656, 658, 670, 672, 674, 676, 678, 690, 692, 694, 696, 698, 701, 703, 705, 707, 709, 721, 723, 725, 727, 729, 741, 743, 745, 747, 749, 761, 763, 765, 767, 769, 781, 783, 785, 787, 789, 810, 812, 814, 816, 818, 830, 832, 834, 836, 838, 850, 852, 854, 856, 858, 870, 872, 874, 876, 878, 890, 892, 894, 896, 898, 901, 903, 905, 907, 909, 921, 923, 925, 927, 929, 941, 943, 945, 947, 949, 961, 963, 965, 967, 969, 981, 983, 985, 987, 989, 1010, 1012, 1014, 1016, 1018, 1030, 1032, 1034, 1036, 1038, 1050, 1052, 1054, 1056, 1058, 1070, 1072, 1074, 1076, 1078, 1090, 1092, 1094, 1096, 1098, 1210, 1212, 1214, 1216, 1218, 1230, 1232, 1234, 1236, 1238, 1250, 1252, 1254, 1256, 1258, 1270, 1272, 1274, 1276, 1278, 1290, 1292, 1294, 1296, 1298, 1410, 1412, 1414, 1416, 1418, 1430, 1432, 1434, 1436, 1438, 1450, 1452, 1454, 1456, 1458, 1470, 1472, 1474, 1476, 1478, 1490, 1492, 1494, 1496, 1498, 1610, 1612, 1614, 1616, 1618, 1630, 1632, 1634, 1636, 1638, 1650, 1652, 1654, 1656, 1658, 1670, 1672, 1674, 1676, 1678, 1690, 1692, 1694, 1696, 1698, 1810, 1812, 1814, 1816, 1818, 1830, 1832, 1834, 1836, 1838, 1850, 1852, 1854, 1856, 1858, 1870, 1872, 1874, 1876, 1878, 1890, 1892, 1894, 1896, 1898, 2101, 2103, 2105, 2107, 2109, 2121, 2123, 2125, 2127, 2129, 2141, 2143, 2145, 2147, 2149, 2161, 2163, 2165, 2167, 2169, 2181, 2183, 2185, 2187, 2189, 2301, 2303, 2305, 2307, 2309, 2321, 2323, 2325, 2327, 2329, 2341, 2343, 2345, 2347, 2349, 2361, 2363, 2365, 2367, 2369, 2381, 2383, 2385, 2387, 2389, 2501, 2503, 2505, 2507, 2509, 2521, 2523, 2525, 2527, 2529, 2541, 2543, 2545, 2547, 2549, 2561, 2563, 2565, 2567, 2569, 2581, 2583, 2585, 2587, 2589, 2701, 2703, 2705, 2707, 2709, 2721, 2723, 2725, 2727, 2729, 2741, 2743, 2745, 2747, 2749, 2761, 2763, 2765, 2767, 2769, 2781, 2783, 2785, 2787, 2789, 2901, 2903, 2905, 2907, 2909, 2921, 2923, 2925, 2927, 2929, 2941, 2943, 2945, 2947, 2949, 2961, 2963, 2965, 2967, 2969, 2981, 2983, 2985, 2987, 2989, 3010, 3012, 3014, 3016, 3018, 3030, 3032, 3034, 3036, 3038, 3050, 3052, 3054, 3056, 3058, 3070, 3072, 3074, 3076, 3078, 3090, 3092, 3094, 3096, 3098, 3210, 3212, 3214, 3216, 3218, 3230, 3232, 3234, 3236, 3238, 3250, 3252, 3254, 3256, 3258, 3270, 3272, 3274, 3276, 3278, 3290, 3292, 3294, 3296, 3298, 3410, 3412, 3414, 3416, 3418, 3430, 3432, 3434, 3436, 3438, 3450, 3452, 3454, 3456, 3458, 3470, 3472, 3474, 3476, 3478, 3490.
Distribution of the remainders when the numbers in this family are divided by n=2, 3,..., 11. (I took into account 4394529 values, from 1 to 989898989).
| n\r | 0 | 1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2034504 | 2360025 | 2 | ||||||||
| 3 | 1464847 | 1464839 | 1464843 | 3 | |||||||
| 4 | 813802 | 1416015 | 1220702 | 944010 | 4 | ||||||
| 5 | 878905 | 878906 | 878906 | 878906 | 878906 | 5 | |||||
| 6 | 678169 | 786674 | 678170 | 786678 | 678165 | 786673 | 6 | ||||
| 7 | 627791 | 627792 | 627790 | 627789 | 627790 | 627789 | 627788 | 7 | |||
| 8 | 406901 | 660808 | 651041 | 472005 | 406901 | 755207 | 569661 | 472005 | 8 | ||
| 9 | 490598 | 485964 | 490317 | 486771 | 489084 | 488281 | 487478 | 489791 | 486245 | 9 | |
| 10 | 406900 | 472005 | 406901 | 472005 | 406901 | 472005 | 406901 | 472005 | 406901 | 472005 | 10 |
| 11 | 427280 | 374177 | 420325 | 384872 | 406756 | 400215 | 390883 | 415331 | 377749 | 425419 | 371522 |
A pictorial representation of the table above
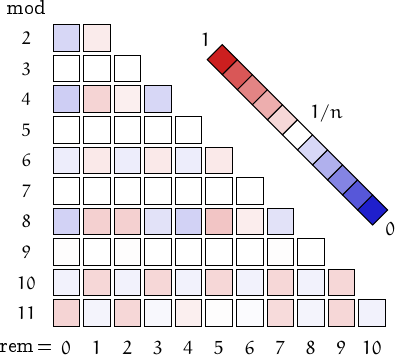
Imagine to divide the members of this family by a number n and compute the remainders. Should they be uniformly distributed, each remainder from 0 to n-1 would be obtained in about (1/n)-th of the cases. This outcome is represented by a white square. Reddish (resp. bluish) squares represent remainders which appear more (resp. less) frequently than 1/n.
e-mail: info -at- numbersaplenty.com • Privacy notice • engine limits